Spark transformation算子之coalesce&&repartition
本文共 2333 字,大约阅读时间需要 7 分钟。
coalesce
def coalesce(numPartitions: Int, shuffle: Boolean = false,partitionCoalescer:Option[PartitionCoalescer] = Option.empty)(implicit ord: Ordering[T] = null): RDD[T]
一、功能介绍
coalesce算子最基本的功能就是返回一个numPartitions个partition的RDD。
二、使用及注意事项
这个算子的结果默认是窄依赖,举个例子
coalesce(100)
如果你想把1000个partition减少到100个partition,此时不会发生shuffle,而是每一个你设定的新partition都会替代原来的10个partition。如果初始的最大partition是100个,而你想用coalesce(1000)把partition数增至1000,这是不行的。
现在有一个需求,需要将某一个文件做ETL,最后想输出成一个文件,你会怎么办呢?这样么?val logs=sc.textFile(args(0),6)//你想初始化6个分区,并行执行,之后再合并成1个文件logs.map(x=>{ if(x.split("\t").length==72){ val clean=parse(x) //此处是进行了ETL clean } }).coalesce(2).saveAsTextFile(args(1)) 如果你同意的话,可以写个demo测试一下,你会发现,仅仅有一个task!在生产上这是绝对不行!因为上述ETL的spark job仅仅有一个stage,你虽然初始化RDD是设定的6个partition,但是在action之前你使用了.coalesce(1),此时会优先使用coalesce里面的partition数量初始化RDD,所以仅仅有一个task。生产中文件很大的话,你就只能用两个节点处理,这样无法发挥集群的优势了。解决:要在coalesce中加shuffle=tule
val logs=sc.textFile(args(0),6)logs.map(x=>{ if(x.split("\t").length==72){ val clean=parse(x) //此处是进行了ETL clean } }).coalesce(2,shuffle = true).saveAsTextFile(args(1)) 这样,我们就会有两个stage,stage1是6个并行高速ETL处理,stage2是通过shuffle合并成2个文件
如下图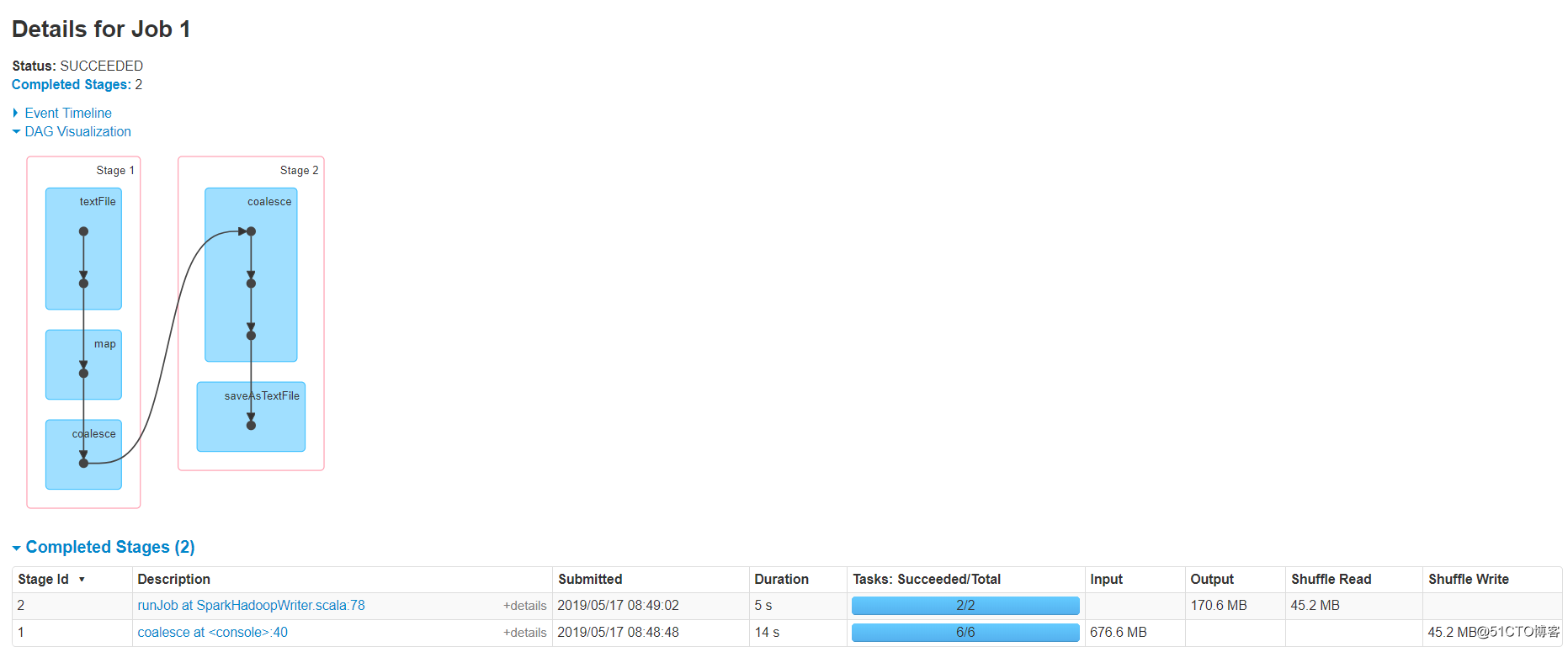 我们知道了,可以手动设定shuffle的发生,那么问题来了,刚刚我们不能将初始化的分区数变大,如果加上shuffle可不可以呢?答案是可以的~如果出事RDD为100个分区,你觉得并行度不够,你可以coalesce(1000,shuffle = true),将分区数增加到1000(默认hash partitioner进行重新),当然你也可以使用自定义分区器,但是一定要序列化。
我们知道了,可以手动设定shuffle的发生,那么问题来了,刚刚我们不能将初始化的分区数变大,如果加上shuffle可不可以呢?答案是可以的~如果出事RDD为100个分区,你觉得并行度不够,你可以coalesce(1000,shuffle = true),将分区数增加到1000(默认hash partitioner进行重新),当然你也可以使用自定义分区器,但是一定要序列化。 三、总结
- coalesce算子默认只能减少分区数量,但是可以通过开启shuffle增加分区数量
- coalesce的作用常常是减少分区数,已达到输出时合并小文件的效果。
- 在一个stage中,coalesce中设定的分区数是优先级最高的,如果想增加并行度,并合并文件,那么请开启coalesce中的shuffle,这样就会变成两个stage。达到并行且合并的效果。
repartition
/** * Return a new RDD that has exactly numPartitions partitions. * * Can increase or decrease the level of parallelism in this RDD. Internally, this uses * a shuffle to redistribute data. * * If you are decreasing the number of partitions in this RDD, consider using `coalesce`, * which can avoid performing a shuffle. * * TODO Fix the Shuffle+Repartition data loss issue described in SPARK-23207. */ def repartition(numPartitions: Int)(implicit ord: Ordering[T] = null): RDD[T] = withScope { coalesce(numPartitions, shuffle = true) } 这个算子前后是一个宽依赖,字面就是重新分区的意思,与coalesce不同,repartition一定会将分区变成numPartitions个的!通过看源码可知,它底层时调用的coalesce算子,并且使用该算子一定会shuffle。
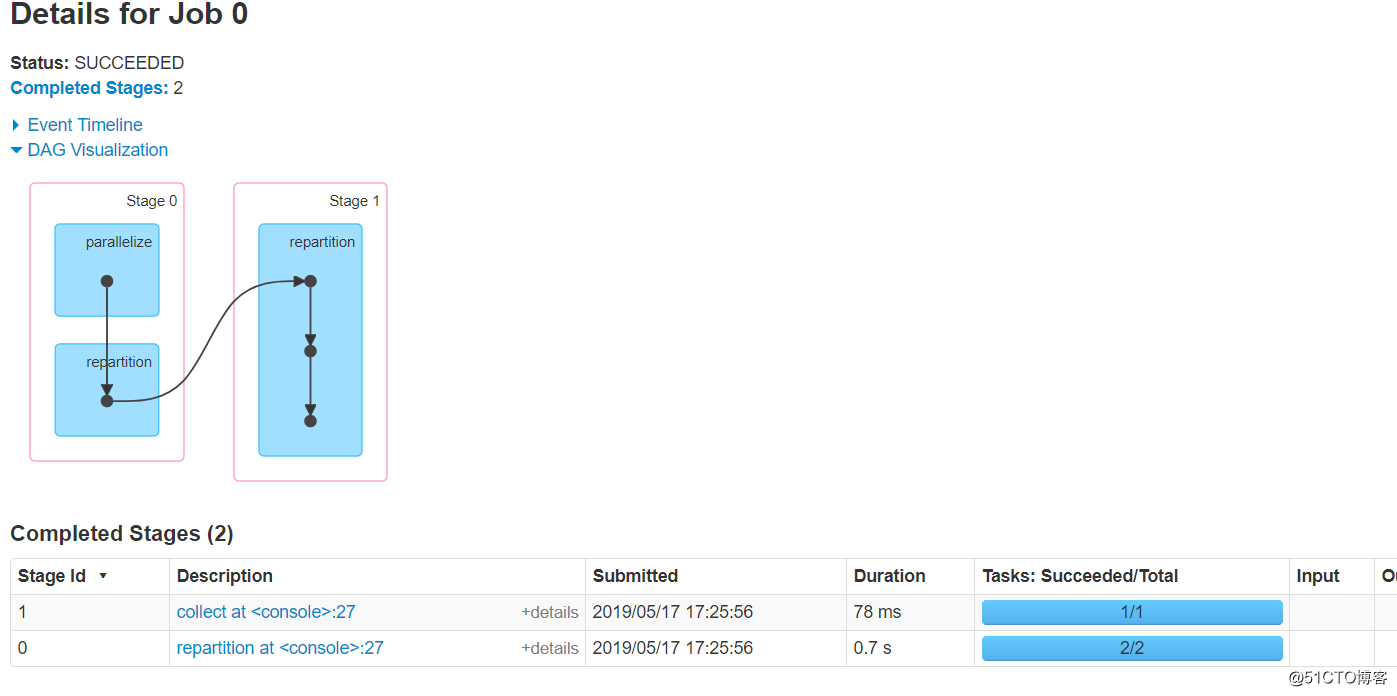
总结
- 返回一个重新分区的RDD,并一定会shuffle
- 我们一般用这个就是为了增加分区数,提高并行度!
转载于:https://blog.51cto.com/14309075/2396421
你可能感兴趣的文章
限制容器的 Block IO - 每天5分钟玩转 Docker 容器技术(29)
查看>>
cocos2dx下的A星算法
查看>>
RabbitMQ的应用场景以及基本原理介绍(转)
查看>>
Nginx:413 Request Entity Too Large解决
查看>>
飘雪代码2枚
查看>>
项目微管理3 - 面试
查看>>
友元函数和友元类
查看>>
SpringMVC中CRUD实例
查看>>
java-jmx使用
查看>>
Win8Metro(C#)数字图像处理--2.15图像霓虹效果
查看>>
Expo大作战(十七)--expo结合哨兵(sentry)进行错误异常记录
查看>>
vue.js入门学习
查看>>
第8件事 3步打造产品的独特气质
查看>>
debug-stripped.ap_' specified for property 'resourceFile' does not exist
查看>>
利用MapReduce计算平均数
查看>>
scala-05-map映射
查看>>
Spring Boot - how to configure port
查看>>
右键添加复制路径选项
查看>>
DocFetcher 本机文件搜索工具
查看>>
ambassador 学习三 限速处理
查看>>